SafetyTech Catalogue
We are building the world’s largest network of safety technology partners.
Find the right partner for you. Get in touch if we can help.
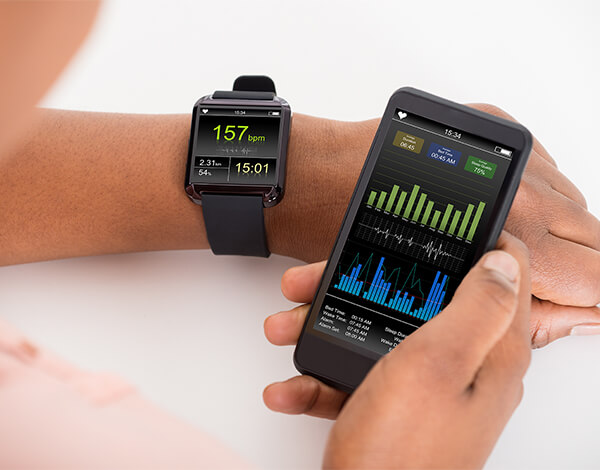

These technologies are specifically aimed towards the collection of worksite data as well as worker behavioral or biometric data to drive safety outcomes.
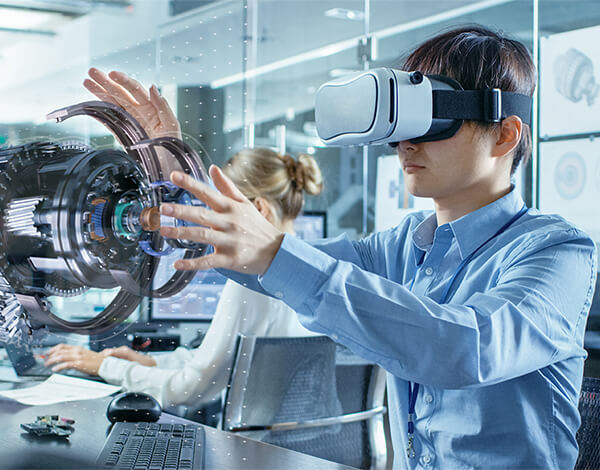

Emerging technologies that utilize a variety of digital immersion or overlays to provide an interactive experience. You can simulate on-the-job scenarios or connect with remote workers as well as external references.
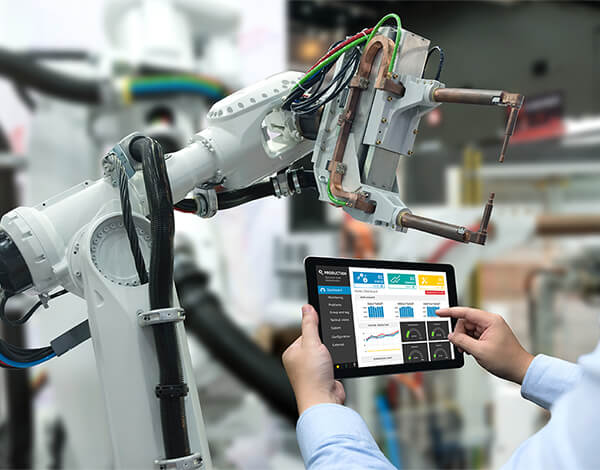

Platform-based solutions that can identify trends, patterns, and anomalies within large datasets in order to predict safety indicators, to provide organizations with actionable insights.










Asset tracking is the process of monitoring physical assets such as products, merchandise, supplies, or the transport vehicle itself. This can be done using scanned barcodes, GPS, or RFID technology. It implies keeping track of physical assets whether they are in storage or traveling within the company or beyond. An effective asset tracking system can reduce loss and theft, keep administrative costs down, and improve both accountability as well as customer service.

Chemical Exposure is described as both the amount of, and the frequency with which a chemical substance reaches a person, group of people, or the environment. Some of the risks of chemical exposure are skin irritation, respiratory problems, intoxication, and liver damage among others.
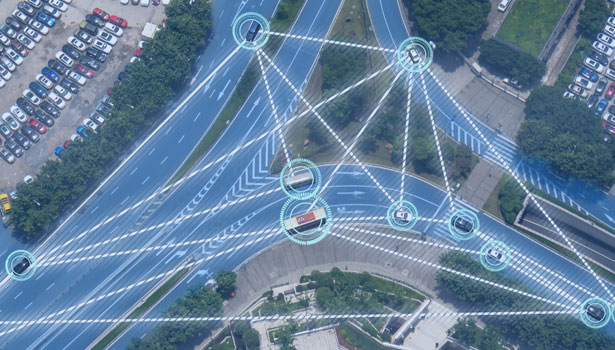
Vehicle Collision Avoidance systems help avoid vehicle to vehicle, vehicle to infrastructure, or vehicle to people collisions. This technology is often used hand in hand with Proximity Detection.

Confined Space refers to any place, including any container, chamber or any other similar space which, by virtue of its enclosed nature, creates conditions that give rise to a likelihood of an accident, harm or injury of such a nature as to require emergency action.
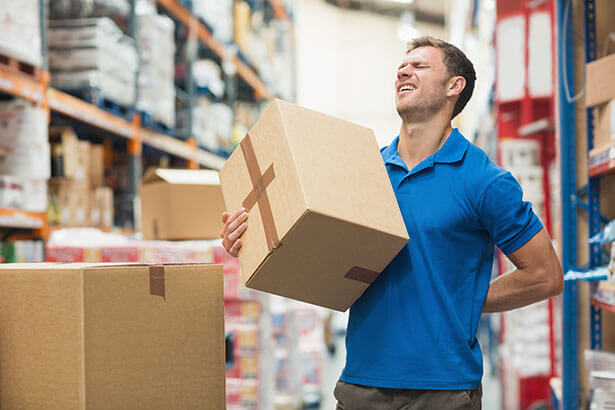

Both ergonomic injuries and Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs) are pain in the human musculoskeletal system, including the joints, ligaments, muscles, nerves, tendons, and structures that support limbs, the neck and the back. They can be caused by awkward, uncomfortable, or sustained positions,repetitive movements, forceful exertion or strain, contact pressure or exposure to vibration.
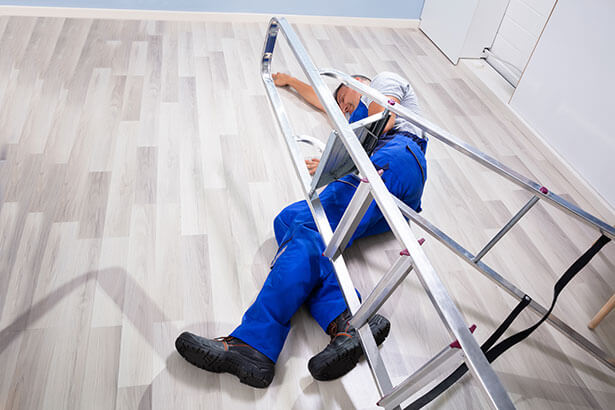

Working at an elevation means work in any place where, if precautions are not taken, a person could fall a distance liable to cause personal injury. A person working from an elevation (i.e. above ground/floor level) could fall from an edge, through an opening or fragile surface, or could fall from ground level into an opening in a floor or a hole in the ground.
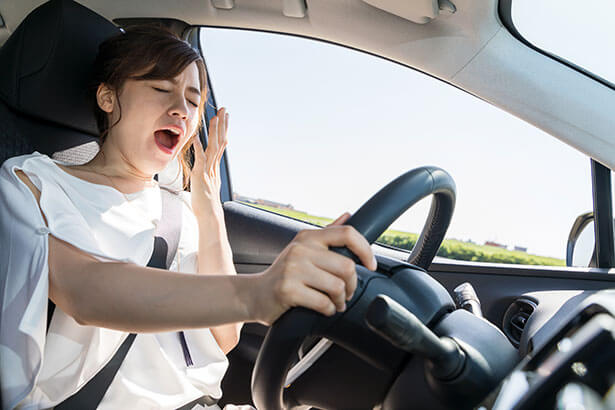

Industrial fatigue is a normal physiological reaction to exertion, lack of sleep, boredom, changes to sleep-wake schedules, or stress. It can be referred to as weariness, tiredness, exhaustion, or lethargy, which are all linked to a lack of energy and focus which can lead to accidents, injuries, or worse.
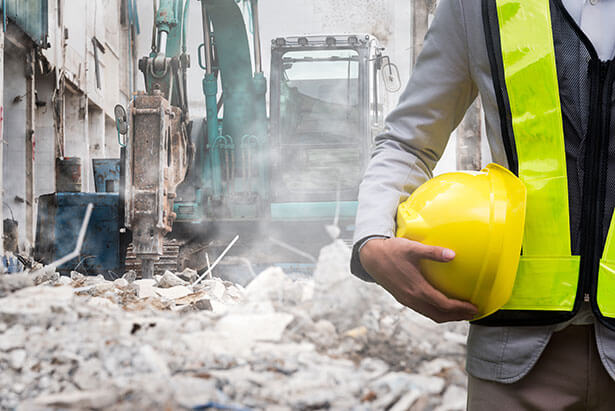

Hazardous areas are spaces where the atmosphere contains, or may contain, flammable or explosive gases, dusts or vapors, and radiation beyond permissible limits.
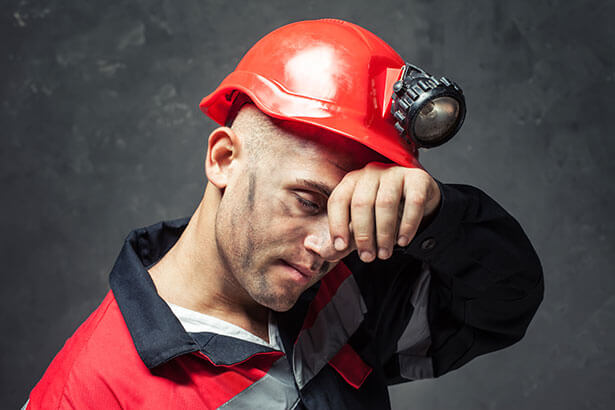

Heat exposure is demonstrated by elevated body temperature, hot, dry skin, lack of sweating, and neurological symptoms such as paralysis, headache, vertigo, and unconsciousness. It can also cause heat cramps, heat exhaustion, and heat stroke, which may lead to death.
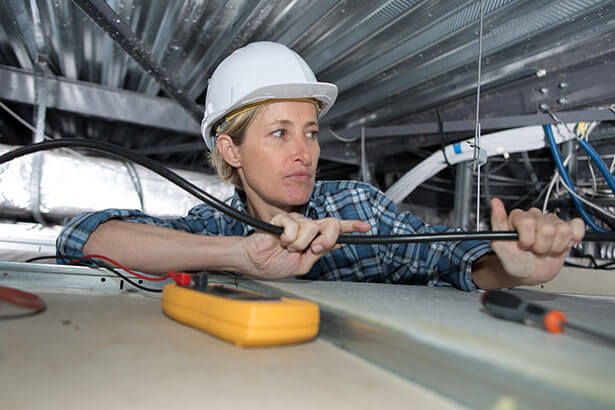

A Lone Worker (LW) is an employee who performs an activity in isolation from other workers, and without close or direct supervision. Such staff may be exposed to risk because there is no-one to assist him/her in case of a complication or incident.

If workers are exposed to noise or vibrations in the workplace on a regular basis over time such exposure may cause permanent inner ear damage leading to hearing loss. Both length of exposure and decibel level are considered in assessing risk; in general if shouting is needed to be heard, the sound levels are within the range of noise that can cause damage.
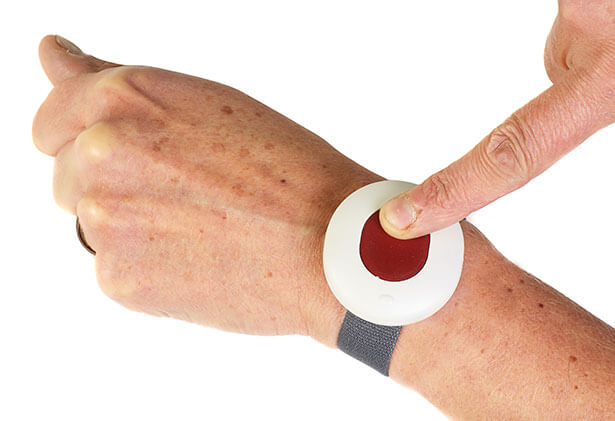

In any dangerous circumstance, employees can use a discrete panic button to send an SOS alert, which will immediately notify the emergency response team about their location and distress.
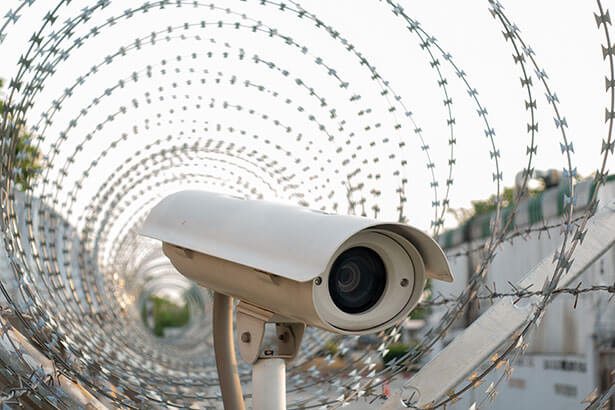

Perimeter protection systems monitor large areas via technology to ensure the safety of workers, restricting access and with sensors triggering an alarm in the case of an intrusion. Options exist to protect work sites from theft as well as natural disasters such as hurricanes.
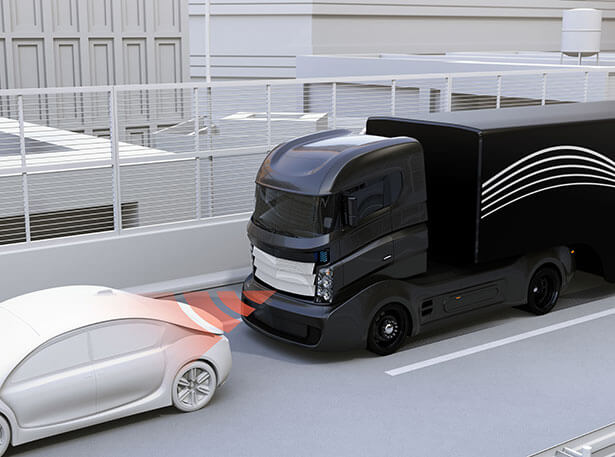

When vehicles and people work in the same spaces, this may result in an accident or collision. A Proximity Detection System is able to stop machine motion and/or send a warning signal to the machine operator when it detects a person or object in the machine’s path. This technology is often used in combination with Collision Avoidance systems, but can also be relevant to generate warnings if a worker gets too close to a burner operating at high heat, for example.

Remote Assistance enables off-site workers to collaborate with information experts thanks to augmented reality/audio/video communication. Experts can view exactly what a remote worker is able to view and share their inputs to reduce/eliminate risk.

The goal of access control is to minimize the risk of unauthorized access to physical and logical systems. This is a fundamental component of security compliance programs to - among other things - protect confidential information such as customer data.
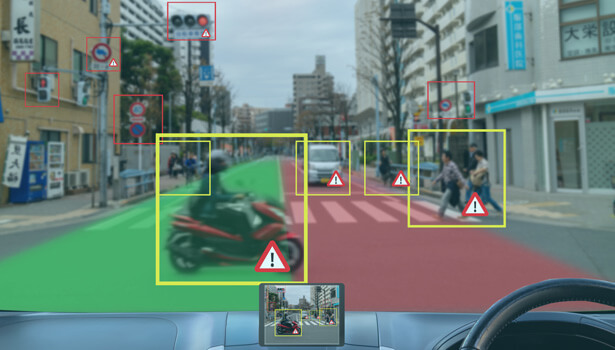
Situational awareness refers to being aware of what is happening around oneself in terms of where you are, where you are supposed to be, and whether anyone or anything around you is a threat to your health and safety.

Slips are the result of too little friction or a lack of traction between the footwear and the floor surface. A trip is the result of a foot striking or colliding with an object, which causes a loss in balance, and usually a fall.

Whole body or hand-transmitted vibrations are one of the mechanical hazards that can be found in industries such as mining & metals or oil & gas. Hand-Arm Vibration Syndrome (HAVS), for instance, is caused by vibration damage that may occur in the fingers, hands, and arms while working with vibrating tools or machinery.

Visual Inspection devices improve safety by automating the need to detect personnel protective equipment (PPE), safety gears, and deviation from standard operating procedures. They provide alerts and warnings when non-compliant equipment or procedures are detected. Using a drone and an iPad can lead to 100x more observations in a faster process, and simplifying access to otherwise hard to reach places such as transmission poles, or sites that cover large geographic areas.

Worker Safety Monitoring systems keep track of lone workers or workers in dangerous environments to ensure their safety. Any technology used to this end should be adapted, and functional within the work environment (e.g. remote lone workers may not have good network coverage or will require long-lasting batteries for any safety monitoring device).




